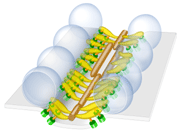
Schematic of the active zone
of
the
frog's neuromuscular
junction
inferred from models
generated by
EM3D.
|
|
Success Stories
EM3D's scheme for the automatic alignment of tilt-images is described.
Ress, D., Harlow, M.L., Schwarz, M., Marshall, R.M., and U.J. Mc Mahan. Automatic acquisition of fiducial markers and alignment of images in tilt series for electron tomography.
J. Electron Microscopy 48: 277-287, 1999
|
| |
EM3D is first used for exposing celluar architecture at macromolecular resolution.
Harlow, M.L., Ress, D., Stoschek, A., Marshall, R.M. and McMahan, U.J. The architecture of active zone material at the frog's neuromuscular junction.
Nature 409:479-484, 2001 |
| |
EM3D's method for creating optimal isodensity surface models is described.
Ress, D., Harlow, M.L., Marshall, R.A., and McMahan, U.J. Optimized Method for Isodensity Surface Models Obtained with Electron Microscope Tomography Data. Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2003. Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of IEEE. pp. 774-777, 2003. |
| |
EM3D is used to examine the architecture of the postsynaptic density at brain synapses.
Petersen, J.D., Chen, X., Vinada, L., Dosemeci, A., Lisman, J.E., and Reese, T.S. Distribution of postsynaptic density (PSD)-95 and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II at the PSD.
J. Neuroscience, 23: 11270-11278, 2003.
|
| |
EM3D approach to model generation is detailed.
Ress, D.B., Harlow, M.L., Marshall, R.M. and McMahan, U.J. Methods for generating high-resolution structural models from electron microscope tomography data.
Structure: 12 (10):1763-1774, 2004.
|
|
EM3D is first used for exposing celluar architecture at macromolecular resolution.
Harlow, M.L., Ress, D., Stoschek, A., Marshall, R.M. and McMahan, U.J. The architecture of active zone material at the frog's neuromuscular junction.
Nature 409:479-484, 2001 |
| |
EM3D's method for creating optimal isodensity surface models is described.
Ress, D., Harlow, M.L., Marshall, R.A., and McMahan, U.J. Optimized Method for Isodensity Surface Models Obtained with Electron Microscope Tomography Data. Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2003. Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of IEEE. pp. 774-777, 2003. |
| |
EM3D is used to examine the architecture of the postsynaptic density at brain synapses.
Petersen, J.D., Chen, X., Vinada, L., Dosemeci, A., Lisman, J.E., and Reese, T.S. Distribution of postsynaptic density (PSD)-95 and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II at the PSD.
J. Neuroscience, 23: 11270-11278, 2003.
|
| |
EM3D approach to model generation is detailed.
Ress, D.B., Harlow, M.L., Marshall, R.M. and McMahan, U.J. Methods for generating high-resolution structural models from electron microscope tomography data.
Structure: 12 (10):1763-1774, 2004.
|
| |
Regulation of Synaptic Vesicle Docking by Different Classes of Macromolecules in Active Zone Material.
Szule, Joseph A., Harlow, Mark L., Jung, Jae Hoon, De-Miguel, Francisco F., Marshall, R.M., McMahan, Uel J.
PLOS One, March 13, 2012
|
|
|
Alignment of Synaptic Vesicle Macromolecules with the Macromolecules in Active Zone Material that Direct Vesicle Docking.
Harlow, Mark L., Szule, Joseph A., Xu, Jing, Jung, Hae Hoon, Marshall, R.M, McMahan
PLOS One, 2013
|
| |
Macromolecular connections of active zone material to docked synaptic vesicles and presynaptic membrane at neuromuscular junctions of mouse.
Nagwaney S, Harlow ML, Jung JH, Szule JA, Ress D, Xu J, Marshall RM, McMahan UJ
The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 513(5): 457-68
|
| |
Variable priming of a docked synaptic vesicle
Jae Hoon Jung, Szule JA, Robert M. Marshall, and Uel J. McMahan
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Feb 23; 113(8): E1098–E1107.
|
|
|
|